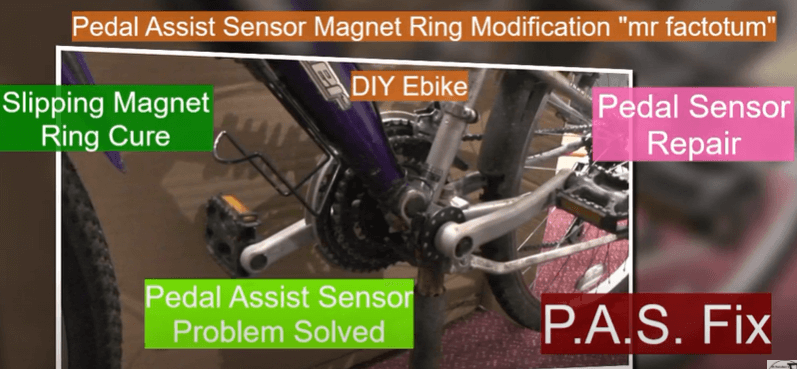
e bike pas
What is an e-bike PAS?
An e-bike PAS (Pedal Assist System) sensor measures how much the user is pedaling and sends a proportional signal to the e-electric bike’s motor to give help. The sensor, which is normally situated on the bike’s bottom bracket or back axle, detects the rotation of the pedal cranks using a magnet and sensor. The degree of help offered by the engine is generally customizable and may be tailored to the rider’s preferences as well as the terrain. Some e-bikes additionally have a throttle, which allows the user to directly regulate the amount of assistance without having to pedal.
Where is e bike pas located?

The PAS (Pedal Assist System) sensor on an e-bike is typically located on the bike’s bottom bracket or rear axle. The sensor uses a magnet and sensor to detect the rotation of the pedal cranks, and sends a corresponding signal to the e-bike’s electric motor to provide assistance.
The sensor may be placed on the chainstay, near the rear hub, or on the bottom bracket of the bike. The location may vary depending on the bike make and model, but it should be located near the crankset.
It’s a good idea to check the manual of your bike or consult the seller/manufacturer to confirm the location of the sensor. Some e-bikes have multiple sensors, one on the left and right crank.
how does an e bike pas work?
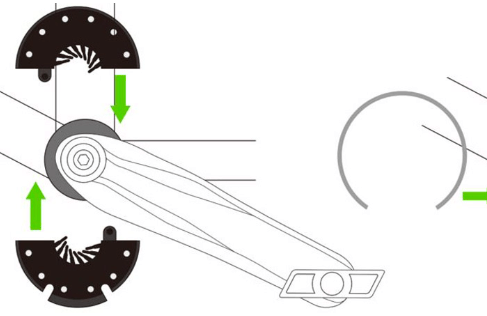
An e-bike PAS (Pedal Assist System) is a device that provides electrical assistance to the rider while they are pedaling. It works by detecting the rider’s pedaling effort and providing a corresponding level of assistance from the electric motor. Here is a more detailed explanation of how an e-bike PAS works:
- Sensor: The PAS sensor is typically located on the bike’s bottom bracket or rear axle, and uses a magnet and sensor to detect the rotation of the pedal cranks. The sensor sends a signal to the e-bike’s controller indicating how much the rider is pedaling.
- Controller: The controller receives the signal from the sensor and uses it to determine how much assistance to provide from the electric motor. The controller also manages the power from the battery to the motor.
- Motor: The electric motor is connected to the rear wheel of the bike and provides the assistance to the rider. The level of assistance can be adjusted by the rider using a button or display on the handlebars, or by the e-bike’s software.
- Battery: The e-bike’s battery provides power to the electric motor. The battery is typically located in the frame of the bike and can be recharged using a standard electrical outlet.
- Throttle: Some e-bikes also come with a throttle, which allows the rider to control the amount of assistance directly, without having to pedal.
When the rider begins to pedal, the PAS sensor detects the rotation of the cranks and sends a signal to the controller, which then sends power from the battery to the motor. The level of assistance can be adjusted by the rider, with higher levels providing more assistance and lower levels providing less.
The PAS is designed to make pedaling easier, particularly on hills or headwinds. It also provides a more natural feeling of riding a bicycle, as the rider is still required to pedal, which can be more enjoyable for some riders.
It’s worth mentioning that the PAS can be used in combination with a throttle, this is known as a “twist and go” system, where the rider can use the pedal assist for efficient riding, and the throttle for starting or when the rider does not want to pedal.
How to fix the e bike pas.
If your e-bike’s PAS sensor is not working, there are a few potential issues that could be causing the problem:
- Loose or dirty connections: Make sure that the connections between the PAS sensor and the e-bike’s controller are clean and secure. If they are dirty, clean them with a dry cloth, if they are loose, try tightening them.
- Dead battery: Check that the battery is charged, if it is not working, try charging it or replacing it.
- Faulty sensor: If the connections and battery are fine, the sensor itself may be faulty and need to be replaced.
- A Magnet or sensor alignment issue: Make sure the magnet which is on the pedal is properly aligned with the sensor.
- Software/ Firmware issue: If the above steps don’t work, it could be a software or firmware issue. Check if there is an update available for your e-bike’s controller and install it if necessary.
It’s always good to refer to the manual of your bike or consult the seller/manufacturer if you have trouble fixing the issue. If you are not comfortable with the troubleshooting, it’s always best to take it to a professional or an e-bike repair shop.
What is the cost of replacing a pedal sensor?
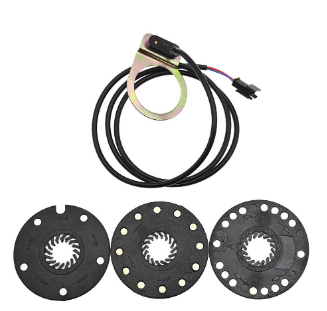
The cost of replacing a PAS (Pedal Assist System) sensor on an e-bike can vary based on several factors, including the e-brand bike’s and model, the position of the sensor, and the cost of labor.
A replacement sensor can cost between $20 and $50 for a simple sensor, but it can cost $100 or more for high-end sensors.
Labor costs vary depending on the bike shop, but can range from $50 to $100.
It’s always a good idea to check with a local e-bike shop or the e-seller/manufacturer bike’s for an estimate on the cost of replacement as well as the availability of the part.
It’s also worth noting that some e-bikes feature two sensors, one on each crank, in which case replacing both sensors would cost extra.
It’s also worth noting that certain sensors are sealed and should not be opened; in this case, the new sensor should arrive as a full unit, which can be more expensive.
It’s always ideal to keep the e-bike well-maintained to avoid costly repairs, and if you detect any problems with the PAS, it’s better to get it checked out.
How long does pedal assist last?
The duration of the battery life on an e-bike with a PAS (Pedal Assist System) can vary greatly depending on a number of factors, including the level of assistance, the terrain, and the rider’s pedaling effort.
The most important factor that affects the battery life is the level of assistance. The higher the level of assistance, the more the electric motor will be used and the more the battery will be drained. In the same way, if the terrain is hilly or the rider is pedaling against a headwind, the electric motor will be used more and the battery will be drained more quickly.
Additionally, the rider’s pedaling effort also plays a role in how quickly the battery is drained. If the rider is pedaling with a high cadence and providing a significant amount of power to the pedals, the electric motor will have to work less and the battery will be drained less quickly.
The capacity of the battery pack is also an important factor. E-bikes with a larger battery pack will have a longer range than those with a smaller battery pack. It’s also important to note that different e-bikes have different battery capacity, some have a bigger battery pack than others.
As an example, a typical e-bike with a 500-watt-hour battery pack and a range of 20-40 miles at a moderate level of assistance, but that can vary depending on the usage, the terrain, and rider’s effort. It’s always good to check the battery level frequently and plan your route accordingly, and also to consider getting a spare battery if you plan to go on longer rides.
Does pedal assist deplete the battery?
Yes, utilizing a PAS (Pedal Assist System) on an e-bike will drain the battery, but the degree of the drain will vary depending on a variety of parameters such as the level of help, the terrain, and the rider’s pedaling effort.
The higher the amount of assistance, the more the electric motor is utilized and the battery is depleted.
Similarly, if the terrain is steep or the rider is pedaling against a headwind, the electric motor will be activated more frequently and the battery will be depleted faster.
Furthermore, the rider’s pedaling effort influences how rapidly the battery drains.
The electric motor will have to work less and the battery will be exhausted less rapidly if the rider cycles with a high cadence and provides sufficient force to the pedals.
It’s also worth noting that different e-bikes have varying battery capacities; some have a larger battery pack than others and hence have a greater range.
It’s always a good idea to check the battery level on a regular basis and plan your route appropriately, and to consider acquiring an extra battery if you want to go on longer journeys.
What happens when the accelerator pedal position sensor fails?
An accelerator pedal position sensor, also known as an accelerator pedal sensor or APP sensor, is a sensor that is used to measure the position of the accelerator pedal and send that information to the engine control module (ECM). It is an essential component of the electronic throttle control system, which is used in many modern vehicles.
When the accelerator pedal position sensor fails, it can cause a variety of issues with the vehicle’s performance. Some of the symptoms of a failed accelerator pedal position sensor include:
- Reduced engine power: The vehicle may not accelerate as quickly or smoothly as it should, or may not accelerate at all.
- Stalling or hesitation: The engine may stall or hesitate when the accelerator pedal is pressed.
- Warning lights: Check engine light or other warning lights may appear on the dashboard.
- Reduced fuel economy: A failed accelerator pedal position sensor can cause the engine to run at an inefficient level, resulting in reduced fuel economy.
- Engine not starting: If the sensor fails completely it may not allow the engine to start.
It’s important to note that a failed accelerator pedal position sensor can also cause other related issues such as the transmission not shifting properly. It’s always best to get your vehicle checked by a professional as soon as possible if you suspect an issue with the accelerator pedal position sensor.
How do you clean a pedal assist sensor?
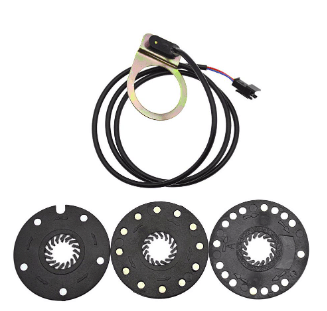
Here are the steps to clean a PAS (Pedal Assist System) sensor on an e-bike:
- Remove the sensor: Depending on the design of the e-bike, the sensor may be located on the bottom bracket or rear axle, it’s important to refer to the manual of your bike or consult the seller/manufacturer to know how to remove the sensor.
- Clean the sensor and magnet: Once the sensor is removed, use a dry cloth or a small brush to remove any dirt or debris that may have accumulated on the sensor and the magnet.
- Clean the connections: Check the connections between the sensor and the e-bike’s controller, if they are dirty, clean them with a dry cloth or a small brush.
- Reinstall the sensor: Once the sensor and connections have been cleaned, reinstall the sensor in its original position and make sure it is properly aligned with the magnet.
- Test the sensor: Once the sensor has been reinstalled, test the e-bike to make sure that the PAS is working properly.
It’s important to keep the sensor and magnet clean and free of dirt and debris to ensure that the PAS is working correctly. It’s a good idea to clean the sensor periodically, especially if you frequently ride on dirty or muddy roads.
It’s important to note that some sensors are sealed and not meant to be opened, if this is the case, it’s best to refer to the manual of your bike or consult the seller/manufacturer for cleaning instructions.
Is pedal help preferable than throttle?
It is a question of personal preference whether to use a PAS (Pedal Assist System) or a throttle on an e-bike.
Both have their own set of benefits and drawbacks.
PAS (Cycle Assist System) assists the cyclist during pedaling, making it simpler to pedal, especially on slopes or in headwinds.
PAS also offers a more natural experience of riding a bicycle because the user must still pedal, which some riders like.
Furthermore, in certain areas, e-bikes must include a pedal assist system in order to be legally ridden on the road.
A throttle, on the other hand, allows the rider to directly regulate the amount of help without the need to pedal. This can be beneficial for riders who prefer to take it easy and allow the electric motor do the most of the work, as well as riders who have difficulties pedaling. It also enables the cyclist to start off from a halt without initially pedaling.
Finally, the decision between PAS and throttle is determined by the rider’s demands and preferences. Some e-bikes include both choices, allowing the rider to select which one to utilize based on the scenario.






