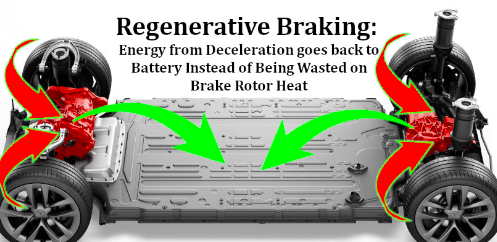
EV regenerative braking
What exactly is EV regenerative braking? What are the pros and cons? everything you need to know about regenerating braking systems in EV.
Regenerative braking is a mechanism seen in electric and hybrid automobiles that absorbs braking energy and stores it in the vehicle’s battery for later use. When the driver hits the brakes, the car’s electric motor serves as a generator, transforming the kinetic energy of the vehicle into electrical energy that is subsequently stored in the battery. This can improve the vehicle’s overall efficiency and expand the range of the electric power.
How does regenerative braking work in electric vehicles?
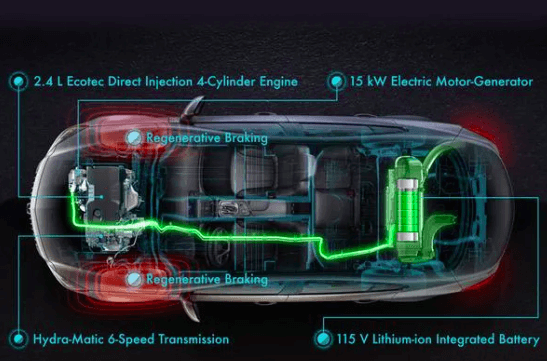
During ev regenerative braking, the electric motor, which is normally attached to the drivetrain, acts as a generator to convert the vehicle’s kinetic energy into electrical energy. This is accomplished by reversing the flow of current through the motor, causing it to create energy rather than move the wheels.
When the driver presses the brake pedal, the control unit sends a signal to the inverter, which causes the current flowing through the motor to reverse direction. This leads the motor to serve as a generator, converting the vehicle’s kinetic energy into electrical energy.
The inverter subsequently transforms the alternating current (AC) supplied by the motor into direct current (DC), which is then stored in the battery.
Simultaneously, the energy gathered during regenerative braking is used to slow the vehicle, minimizing the requirement for friction brakes. The regenerative resistor, which can be modified to regulate the amount of energy released as heat, may be used to alter the amount of energy collected during regenerative braking.
To summarize, regenerative braking in electric vehicles allows the vehicle to catch energy when braking and store it in the battery for later use, decreasing the need for friction brakes and enhancing overall vehicle efficiency.
What are the advantages of using regenerative braking systems?
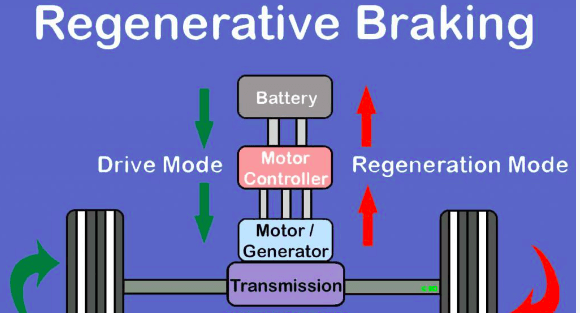
The use of regenerative braking systems in electric cars has various advantages, including:
Enhanced Energy Efficiency:
EV Regenerative braking systems gather and store braking energy, which may then be utilized to power the vehicle. This increases energy efficiency and can assist to prolong the vehicle’s range.
Friction brake wear and tear is reduced:
Regenerative braking systems eliminate the need for standard friction brakes by capturing and storing energy during braking. This reduces friction brake system wear and tear, which can assist to increase brake life and save maintenance costs.
Vehicle Performance Improvements:
Regenerative braking systems can increase vehicle performance by gathering and storing energy when braking. This is because the collected energy may be utilized to power the vehicle later on, extending the range and improving overall efficiency.
Emissions Reductions:
Because regenerative braking systems improve vehicle economy, they can assist to reduce emissions. This is because the car will consume less energy overall, resulting in fewer emissions.
Cost-effective:
Regenerative braking systems save money over time because they eliminate the need for friction brakes, which must be replaced and maintained on a regular basis.
What are the disadvantages of ev regenerative braking?
Regenerative braking systems have a few disadvantages, including:
- Limited effectiveness: Regenerative braking systems are most effective at slowing down a vehicle at low speeds and are less effective at high speeds.
- Reduced brake life: Regenerative braking systems rely on the friction brakes less, which may reduce their lifespan.
- Cost: The cost of regenerative braking systems can be higher than traditional friction braking systems.
- Battery Dependence: Regenerative braking systems require a battery to store the energy generated during braking, which adds to the cost of the vehicle and can also limit the range of electric vehicles.
- Complexity: Regenerative braking systems are more complex than traditional friction braking systems and may require more maintenance.
- Compatibility issues: Some vehicles may not be compatible with regenerative braking systems and may require significant modifications to be installed.
What exactly is ev regenerative braking torque?
Braking using regenerative energy The amount of torque applied to the electric motor during regenerative braking is referred to as torque. Torque is a measure of the force that induces rotation and is commonly expressed in newton-meters (Nm) or pound-feet (Pf) (lb-ft).
The electric motor is employed during regenerative braking to convert the vehicle’s kinetic energy into electrical energy. During this process, the amount of torque supplied to the motor is directly proportional to the quantity of energy collected and stored in the battery.
The quantity of energy collected during braking may be controlled by adjusting the regenerative braking torque.
This can be accomplished by altering the control unit’s settings or the regeneration resistor.
To summarize, regenerative braking torque is the amount of torque supplied to the electric motor during regenerative braking, which has a direct impact on the quantity of energy captured and stored in the battery. It may be modified to improve the vehicle’s overall efficiency.
During regenerative braking, which component converts AC to DC?
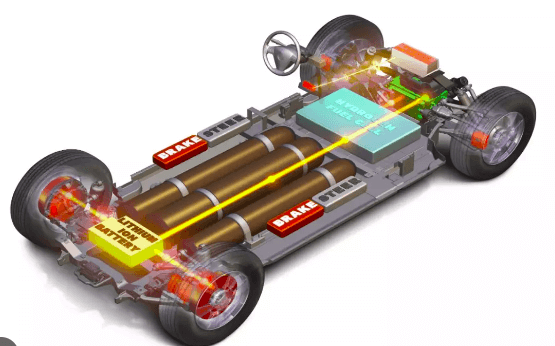
The electric motor creates alternating current (AC) power during regenerative braking. This electricity must be converted into direct current (DC) before it can be stored in the battery or utilized to power other vehicle systems. An inverter is the component that transforms the AC power generated by the motor into DC electricity.
The inverter is a critical component of a regenerative braking system; it transforms the alternating current (AC) power generated by the motor into direct current (DC) electricity that may be stored in the battery. It also regulates the flow of power between the motor, battery, and other vehicle components.
In most cases, the inverter is a separate component that is connected to the electric motor and the battery, but in certain cases, it can be integrated into the motor controller or a power management system.
It’s worth mentioning that in certain systems, the AC power supplied by the motor is converted directly to DC power in the motor controller; this technique is more efficient since it minimizes power loss during the conversion process.
Do ev regenerative brakes use magnets?
Yes, regenerative braking systems use magnets as part of the electric motor. In Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) , which is one of the types of electric motors commonly used in regenerative braking systems, the rotor is typically equipped with a set of permanent magnets. The magnets create a magnetic field that interacts with the magnetic field created by the stator windings, causing the rotor to rotate.
During regenerative braking, the motor works in reverse and acts as a generator. The rotation of the rotor caused by the vehicle’s motion generates a current in the stator windings, which is then sent to the inverter and battery. The interaction between the magnetic field of the rotor and the stator windings is what allows the motor to convert the kinetic energy of the vehicle into electrical energy.
It’s also worth noting that some regenerative braking systems use Permanent Magnet AC (PMAC) motors, which have a rotor equipped with permanent magnets that interacts with the stator windings to generate electricity.
In summary, regenerative braking systems use electric motors that have permanent magnets in their rotor to convert the kinetic energy of the vehicle into electrical energy during braking.
How does a regenerative resistor work?

A regenerative resistor is a component of a regenerative braking system that converts electrical energy produced while braking into heat. It functions by dissipating electrical energy as heat and is linked in series with the electric motor and the inverter.
When the driver presses the brake pedal, the control unit transmits a signal to the electric motor, which causes it to start producing power. The electricity is then sent to the regenerative resistor, where it is converted into heat. This procedure both slows the car and helps to recharge the battery.
The regenerative resistor is just a variable resistor that can be modified to regulate how much energy is lost as heat. This enables the system to fine-tune the quantity of energy transferred to the battery as well as the amount of energy released as heat.
The size and kind of regeneration resistor will be determined by the unique system and vehicle needs. Some regenerative braking systems employ a single big resistor, while others use a series or parallel connection of numerous smaller resistors.
It’s worth mentioning that not all regenerative braking systems employ a regeneration resistor; some use a different method to govern the amount of energy supplied to the battery, while others can.
Are capacitors used in EV regenerative braking?
Capacitors, in addition to batteries, may be used in some regenerative braking systems to store the energy created during braking. When it comes to energy storage, capacitors, also known as supercapacitors, offer various benefits over batteries. They can charge and discharge considerably faster than batteries and have a significantly better power density. They are also more durable and require less maintenance than batteries.
Capacitors are frequently employed in regenerative braking systems that demand high power and quick response times, such as those used in hybrid and electric automobiles, as well as in industrial and aerospace applications. They can also be utilized in combination with batteries to increase overall system efficiency.
It should be noted that not all regenerative braking systems employ capacitors; some solely use batteries to store the energy created during braking, and this will depend on the individual system and the vehicle’s requirements.
Which motor is used in EV regenerative braking?
In regenerative braking systems, an electric motor is used as a generator to convert the kinetic energy of the vehicle into electrical energy during braking. The two main types of electric motors used in regenerative braking systems are:
- Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs): These motors are known for their high efficiency and fast response times. They are commonly used in hybrid and electric vehicles, as well as in industrial and aerospace applications.
- Induction Motors: These motors are known for their robustness and reliability. They are commonly used in industrial and automotive applications, and are a popular choice for regenerative braking systems due to their simple and robust design.
The choice of the motor for regenerative braking system will depend on the specific requirements of the vehicle and the design of the system. Some vehicle manufacturers use a specific type of motor, while others may use a combination of different types of motors to achieve the desired performance and efficiency.
It’s also worth noting that some regenerative braking systems use the same motor that propels the vehicle in forward motion as a generator to convert kinetic energy into electricity during braking, while others use a separate motor that is dedicated to regenerative braking.
Is it necessary to maintain regenerative brakes?
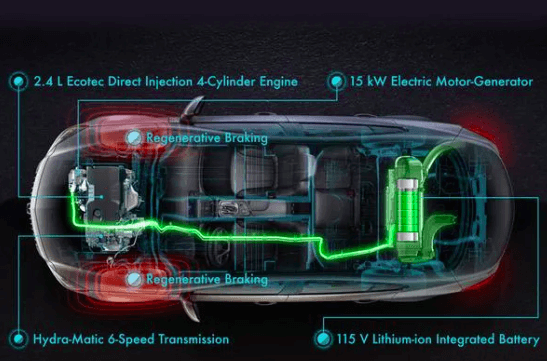
Although regenerative braking systems require less maintenance than traditional friction brakes, they still require regular inspection and maintenance to ensure optimal operation. Some of the maintenance activities that a regenerative braking system may require include: Examining the brake pads and rotors for wear and replacement if necessary. Inspecting the brake lines and hoses for leaks or damage and, if necessary, replacing them.
It’s also worth noting that proper maintenance is essential for the brakes to perform well in a variety of conditions, including snow, and keeping the brake pads, rotors, drums, and other brake components clean, lubricated, and in good condition can help to ensure that the brakes work as well as possible.
To prolong the lifespan of regenerative brakes, verify the manufacturer’s instructions and adhere to the vehicle’s maintenance plan.
It is also critical to handle any warning lights or faults with the brakes as soon as they emerge in order to avoid serious problems in the future.
Is regenerative braking available on all evs?

Regenerative braking systems are standard on the majority of electric vehicles (EVs). Regenerative braking is a fundamental component of electric vehicles that helps to extend the vehicle’s range and economy. It works by converting the kinetic energy of the car while braking into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery, and this accumulated energy can then be used to power the vehicle.
It’s worth mentioning that not all electric vehicles use the same sort of regenerative braking technology, and some are more sophisticated than others. Some cars may also have various amounts of regenerative braking, which may be changed by the driver or handled automatically by the vehicle’s computer.
Does regenerative braking need fuel?

Regenerative braking devices do not use fuel in the traditional sense; instead, they convert the kinetic energy of a moving vehicle into electrical energy that can be stored in a battery, and this accumulated energy can then be used to power the vehicle. Regenerative braking systems are commonly found in electric or hybrid cars, which are powered by electricity or a combination of electricity and fuel.
So, regenerative braking does not burn fuel in the sense of fossil fuels, but it does drain energy from the battery, which is not wasted because it catches energy from the vehicle’s motion and may be utilized to power the vehicle.
Can regenerative braking bring a car to a complete stop?

- Regenerative braking systems can help slow a vehicle, but they are not typically designed to bring a vehicle to a complete stop on their own.
- They can be used in conjunction with standard friction brakes to bring the vehicle to a complete stop.
- Regenerative braking systems convert the kinetic energy of a moving vehicle into electrical energy that may be stored in a battery.
- This stored energy can subsequently be utilised to power the vehicle.
- While regenerative braking can slow a vehicle, it may not be as effective as standard friction brakes in terms of stopping force.
- Both types of brakes are frequently combined into the brake pedal in electric cars, which means that the friction brakes work in concert with the regenerative brakes.
- Do electric vehicles charge while driving? Do Evs lose charge when parked?
- Can an electric SUV tow cargo? What are the pros and cons of Electric SUVs?.
- Top Leading Lithium exporters in the world this 2023?
- What is a lithium ion battery? Everything you should know about lithium ion batteries.
- How to maintain bike chain. Is dry lube better than wet lube?






